So far in this series, we’ve discussed some of the promises around scaling solutions that have yet to hit the market, namely Ethereum sharding. In my most recent post, we covered Rollups as a solution, and we now know that although the technology is very young, Rollups have the potential to provide groundbreaking improvements to the scalability of Ethereum. That post can be found here.
Now, in the penultimate part of our series, we shift our focus to another technology that offers a solution to Ethereum's scaling issue: side-chain solutions. Let’s dive in…
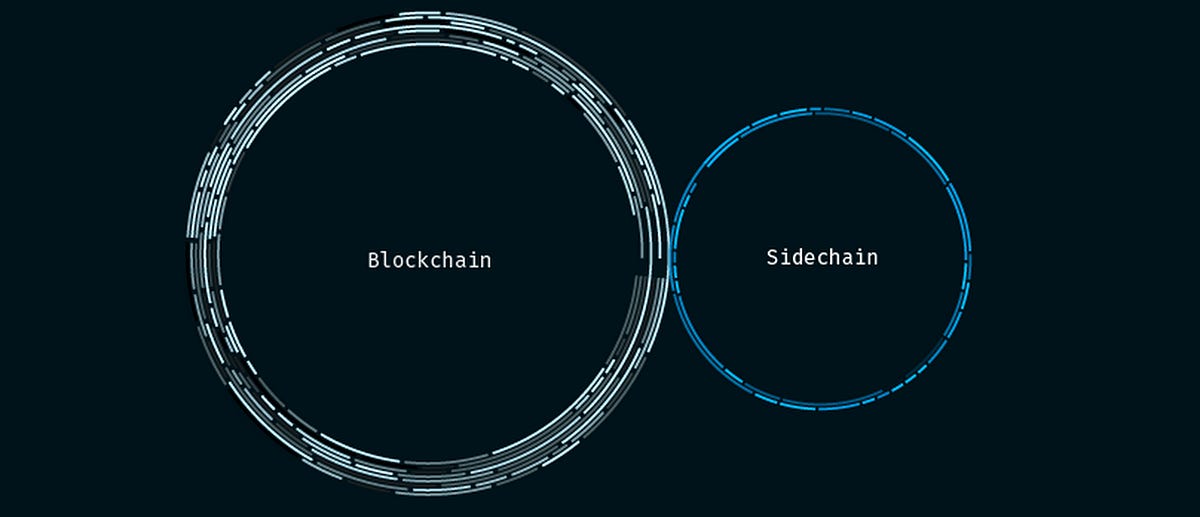
Side-chains as a Solution
By now, hobbyists, as well as crypto veterans, know that Ethereum has the most successful adoption supporting numerous blockchain dApps. Ethereum is currently home to more than 4000 dApps, which is no small feat.
However, the driver of such huge success is not attributed to just Ethereum alone due to its limited scalability and costly gas fees. Scaling solutions like side-chains, which aim to tackle Ethereum's scaling problem, are gaining serious traction.
What are they exactly, and what makes this solution different?
Generally, side-chains are a separate blockchain network that connects to another blockchain via a two-way bridge. They essentially act as a secondary blockchain that runs in parallel to a main chain such as Bitcoin or, in this case, Ethereum. Side-chains can have their consensus algorithms, and as such, these chains need their own miners and validators since they can have their own consensus mechanism. Furthermore, side-chains do not publish state changes or transaction data on Ethereum, and they do not inherit Ethereum's security. As a result they are susceptible to security vulnerabilities such as chain reorgs. These nuances are the main differences between traditional L2 solutions as covered in this series and side-chains as a scaling solution. For a detailed overview of how side-chains work in practice, please see here.
Final thoughts
Side-chains promote developer experimentation through their upgradable architecture; they allow new ideas to be tested and deployed without broad consensus, ultimately contributing to the overall scalability of the solution. Further, on this point, side-chains as a solution do offer faster and cheaper transactions by moving certain types of transactions to another chain resulting in decongestion of the main chain.
If you’re interested in seeing the full extent of side-chains, a number of projects exist and are widely used, with Polygon being the largest side-chain solution achieving nearly 65k transactions per second.
Polygon uses an Ethereum framework called Plasma, which allows the creation of child chains that can process transactions before periodically being finalized on the Ethereum blockchain. Polygon issues its own native token, MATIC, through Proof-of-Stake validators. To get started using the Polygon network, you’ll need to bridge assets after setting up a wallet.
Closing Remarks
Side-chains have the potential to revolutionize the way blockchains operate. They add flexibility and allow developers to experiment with beta releases of software updates before pushing them onto the main chain. If the security mechanisms for side-chains can be improved upon, side-chain solutions hold promise for massive blockchain scalability.
In the next piece, we will continue to explore Ethereum scaling solutions, looking at state-channel solutions next.
If you are an investor or builder in the space and would like to connect, feel free to reach out to me at Ernest@Boldstart.vc or on Twitter @ErnestAddison21.